What Are Protists That Have Animal Like Characteristics Called
What Are Protists That Have Animal Like Characteristics Called
What are protists?

Protists are a diverse collection of organisms that practice not fit into animate being, institute, leaner or fungi groups. While exceptions be, they are primarily microscopic and fabricated up of a single cell (unicellular), according to the educational website CK-12 (opens in new tab) .
Protists are eukaryotes as they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (structures that perform a specific chore).
At 1 time, simple organisms such every bit amoebas and single-celled algae were classified together in a single taxonomic category: the kingdom Protista. Nevertheless, the emergence of better genetic data has since led to a clearer understanding of evolutionary relationships amid dissimilar groups of protists, and this nomenclature arrangement was rendered defunct. Understanding protists and their evolutionary history continues to be a matter of scientific discovery and give-and-take.
Characteristics of protists
All living organisms can be broadly divided into two groups — prokaryotes and eukaryotes — which are distinguished past the relative complexity of their cells. In contrast to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells are highly organized. Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, while all other living organisms — protists, plants, animals and fungi — are eukaryotes, according to the educational website tutors.com (opens in new tab) .
Many diverse organisms including algae, amoebas, ciliates (such as paramecium) fit the general moniker of protist. "The simplest definition is that protists are all the eukaryotic organisms that are not animals, plants or fungi," said Alastair Simpson (opens in new tab) , a professor in the section of biological science at Dalhousie University. The vast majority of protists are unicellular or course colonies consisting of one or a couple of singled-out kinds of cells, according to Simpson. He further explained that there are examples of multicellular protists among brown algae and certain red algae.
Protist cells
Similar all eukaryotic cells, protists take a characteristic primal compartment called the nucleus, which houses their genetic fabric. They also have specialized cellular machinery chosen organelles that execute defined functions inside the cell. Photosynthetic protists such every bit the various types of algae incorporate plastids. These organelles serve every bit the site of photosynthesis (the procedure of harvesting sunlight to produce nutrients in the form of carbohydrates). The plastids of some protists are like to those of plants. Co-ordinate to Simpson, other protists have plastids that differ in the color, the repertoire of photosynthetic pigments and even the number of membranes that enclose the organelle, as in the case of diatoms and dinoflagellates, which establish phytoplankton in the ocean.
Most protists have mitochondria, the organelle which generates energy for cells to utilise. The exceptions are some protists that live in anoxic weather condition, or environments defective in oxygen, according to Astrobiology at NASA (opens in new tab) . They use an organelle called the hydrogenosome (which is a profoundly modified version of mitochondria) for some of their energy production. For example, the sexually transmitted parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which infects the human vagina and causes trichomoniasis, contains hydrogenosomes.
Related: Robert Hooke: English scientist who discovered the cell
Protist feeding habits
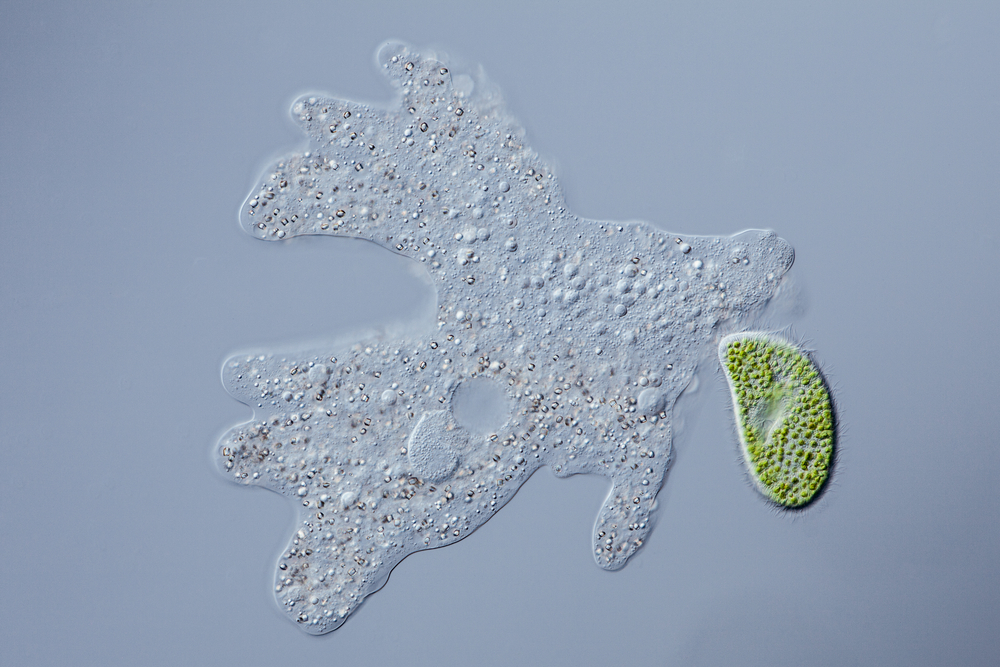

Protists gain diet in a number of ways. Co-ordinate to Simpson, protists can be photosynthetic or heterotrophs (organisms that seek outside sources of food in the form of organic fabric). In plow, heterotrophic protists (opens in new tab) fall into two categories: phagotrophs and osmotrophs. Phagotrophs use their cell body to surround and swallow up nutrient, oftentimes other cells, while osmotrophs blot nutrients from the surrounding surroundings. "Quite a few of the photosynthetic forms are likewise phagotrophic," Simpson told Live Science. "This is probably true of nearly 'algal' dinoflagellates for example. They have their ain plastids, but will also happily eat other organisms." Such organisms are called mixotrophs, reflecting the mixed nature of their nutritional habits.
Protist reproduction
Most protists reproduce primarily through asexual mechanisms co-ordinate to Simpson. This can include binary fission, where a parent cell splits into two identical cells or multiple fission, where the parent cell gives rise to multiple identical cells. Simpson added that most protists probably also accept some kind of sexual wheel, nevertheless, this is only well documented in some groups.
Nomenclature: from Protozoa to Protista and beyond
The classification history of protists traces our agreement of these diverse organisms. Often circuitous, the long history of protist classification introduced two terms, still used today, into the scientific lexicon: protozoa and protists. Nevertheless, the pregnant of these terms has also evolved over fourth dimension.
The observable living world was once neatly divided between plants and animals. But the discovery of diverse microscopic organisms (including what we now know every bit protists and leaner) brought forth the need to understand what they were, and where they fit taxonomically.
The first instinct of scientists was to relate these organisms to plants and animals by relying on morphological characteristics. The term protozoan (plural: protozoa or protozoans), pregnant "early animals," was introduced in 1820 by naturalist Georg A. Goldfuss, according to a 1999 commodity published in the periodical International Microbiology (opens in new tab) . This term was used to describe a collection of organisms including ciliates and corals. By 1845, Protozoa was established as a phylum or subset of the animate being kingdom past German scientist Carl Theodor von Seibold. This phylum included certain ciliates and amoebas, which were described past von Seibold as single-celled animals. In 1860, the concept of protozoans was further refined and they were elevated to the level of a taxonomic kingdom past paleontologist Richard Owen. The members of this Kingdom Protozoa, in Owen'due south view, had characteristics mutual to both plants and animals.
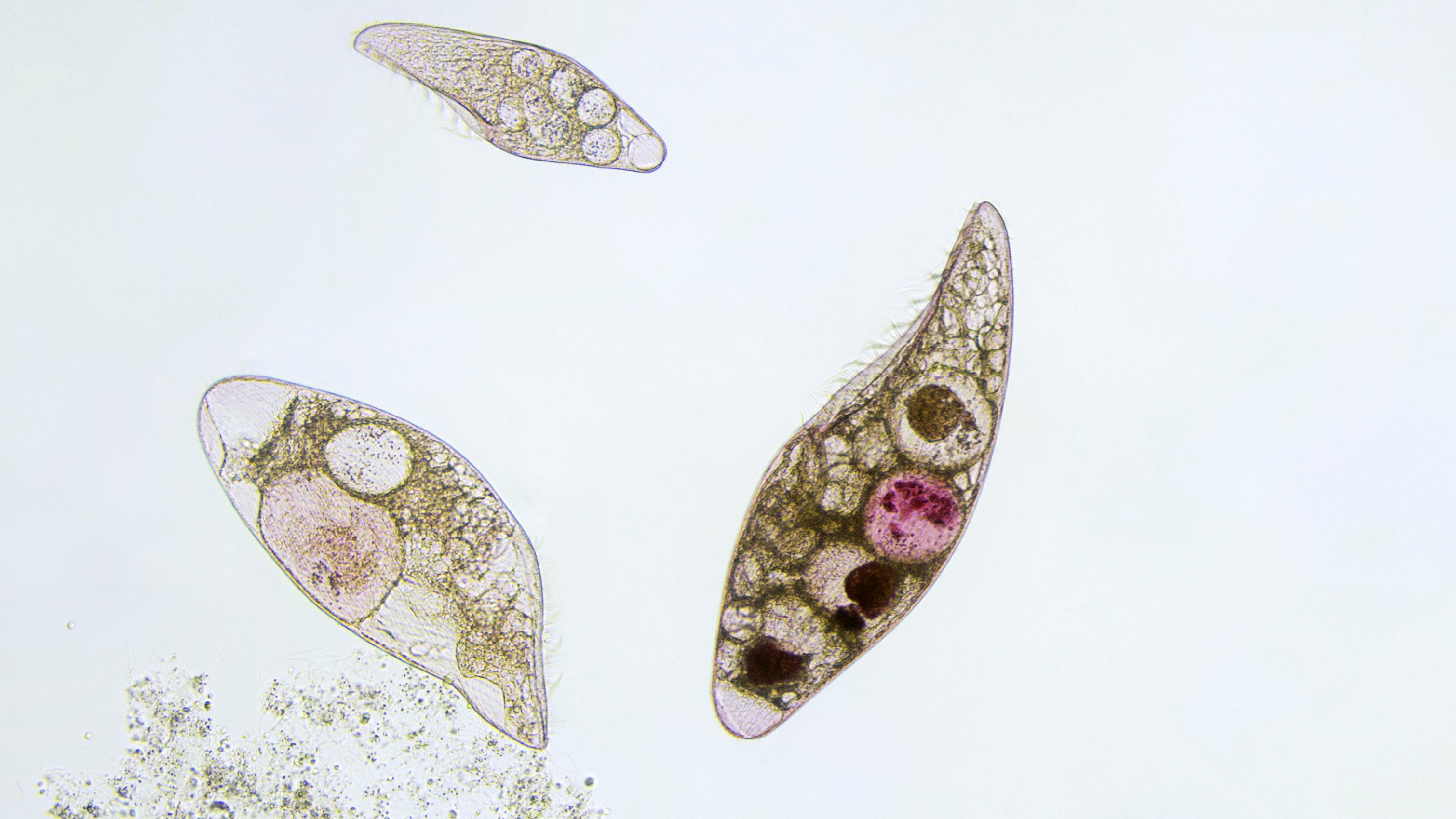
Though the scientific rationale behind each of these classifications unsaid that protozoans were rudimentary versions of plants and animals, in that location was no scientific evidence of the evolutionary relationships between these organisms (International Microbiology, 1999). Co-ordinate to Simpson, present "protozoa" is a term of convenience used in reference to a subset of protists, and is not a taxonomic group. "In order to exist called a protozoan, they [protists] accept to exist non-photosynthetic and not very fungus-like," Simpson told Live Science.
The term protista, meaning "the first of all or primordial" was introduced in 1866 past German scientist Ernst Haeckel. He suggested Protista as a third taxonomic kingdom, in addition to Plantae and Animalia, consisting of all "primitive forms" of organisms, including leaner (International Microbiology, 1999).
Since then, the kingdom Protista has been refined and redefined many times. Different organisms moved in and out (notably, bacteria moved into a taxonomic kingdom of their own). American scientist John Corliss proposed one of the modern iterations of Protista in the 1980s. His version included the multicellular red and chocolate-brown algae, which are considered to be protists even today.
Scientists, oftentimes concurrently, have debated kingdom names and which organisms were eligible (for instance, versions of yet another kingdom, Protoctista had been proposed over the years). Notwithstanding, it is important to note the lack of correlation between taxonomy and evolutionary relationships in these groupings. According to Simpson, these groupings were not monophyletic, meaning that they did non stand for a single, whole branch of the tree of life; that is, an ancestor and all of its descendants.
Today's nomenclature has shifted away from a system congenital on morphology to one based on genetic similarities and differences. The upshot is a family unit tree of sorts, mapping out evolutionary relationships betwixt various organisms. In this system, there are three main branches or "domains" of life: Leaner, Archaea (both prokaryotic) and Eukarya (the eukaryotes).
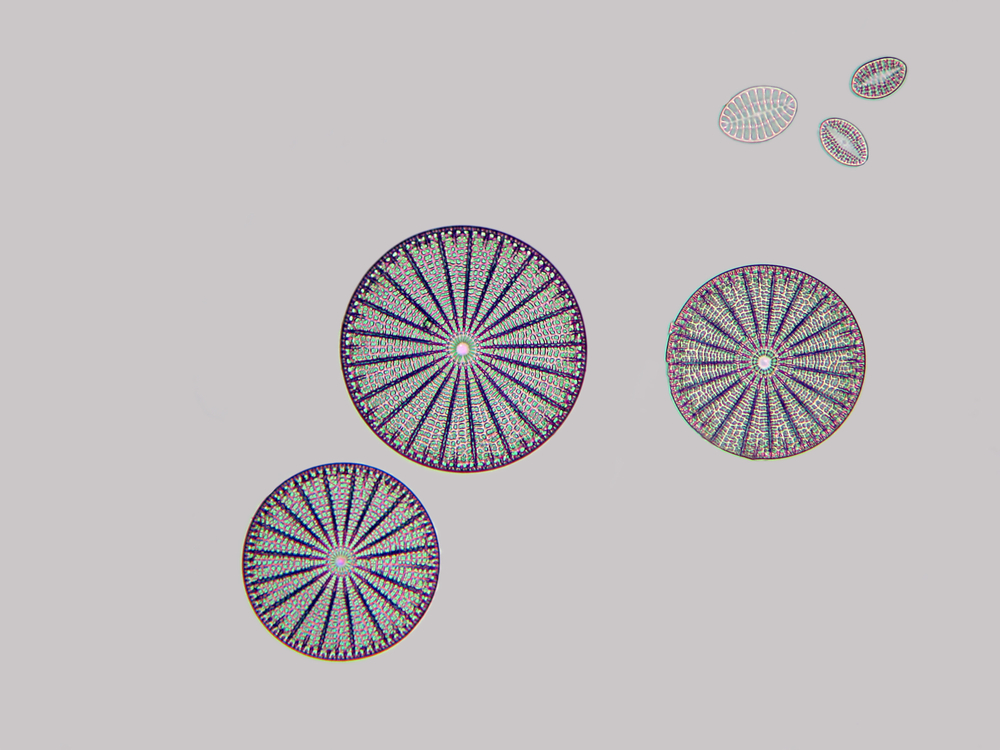
Inside the eukaryotic domain, the protists are no longer a unmarried group. They have been redistributed amongst different branches of the family tree. According to Simpson, nosotros at present know virtually of the evolutionary relationships among protists, and these are often counterintuitive. He cited the example of dinoflagellate algae, which are more closely related to the malaria parasite than they are to diatoms (another group of algae) or fifty-fifty to state plants.
Yet, there are pressing questions that remain. "Nosotros simply don't know what the earliest split was among the lineages that led to living eukaryotes," Simpson told Alive Scientific discipline. This point is chosen the "root" of the eukaryotic tree of life. Pinpointing the root will cement the understanding of eukaryotic origins and their subsequent evolution. Equally author Tom Williams said in a 2014 article published in the periodical Electric current Biology (opens in new tab) , "For the eukaryotic tree, the root position is critical for identifying the genes and traits that may have been present in the bequeathed eukaryote, for tracing the evolution of these traits throughout the eukaryotic radiation, and for establishing the deep relationships among the major eukaryotic groups."
The importance of protists
are responsible for a variety of human diseases including malaria, sleeping sickness (opens in new tab) , amoebic dysentery and trichomoniasis (opens in new tab) . Malaria in humans is a devastating disease. It is acquired by five species of the parasite Plasmodium, which are transmitted to humans by female person Anopheles mosquitoes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (opens in new tab) (CDC). The species Plasmodium falciparum infects red blood cells, multiplies speedily and destroys them. Infection tin can also cause ruby blood cells to stick to the walls of small blood vessels. This creates a potentially fatal complexity chosen cerebral malaria (co-ordinate to the CDC).
The World Health Organization (WHO) states that Plasmodium falciparum is the most prevalent and lethal to humans. Co-ordinate to their recent malaria fact sheet (opens in new tab) , in 2022 at that place were an estimated 627,000 deaths due to malaria in the world, the majority of which (90 percent) occurred in Africa. Sure strides have been made in reducing the rates of incidence (occurrence of new cases) and mortality rates in function by supplying insecticide-treated mosquito nets, spraying for mosquitoes and improving diagnostics. According to the WHO "In 2022, 26 countries reported fewer than 100 indigenous cases of the disease, up from half-dozen countries in 2000".The WHO has a goal of eliminating malaria in at least 35 countries by 2030.
Protists also play an important role in the environment. According to CK-12, plant-similar protists produce almost half of the oxygen on Earth through photosynthesis. Protists human action as decomposers and help in recycling nutrients through ecosystems, according to the educational website Biology Online (opens in new tab) . In improver, protists in various aquatic environments, including the open h2o, waterworks and sewage disposal systems feed upon, and control bacterial populations "If you took all the protists out of the earth, the ecosystem would collapse really chop-chop," Simpson said.
Additional resource
If y'all would like to larn more almost protists check out this informative lesson on the educational website Written report.com (opens in new tab) , you tin even take a quiz at the finish to test your knowledge. Read more than about how protists are beneficial to humans in this article from the science news site AllThingsNature (opens in new tab) . If you're notwithstanding wanting more, head over to the educational website Lumen Learning (opens in new tab) for even more protist content.
Bibliography
- Caron, David A. "Towards a molecular taxonomy for protists: benefits, risks, and applications in plankton ecology. (opens in new tab) " Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology sixty.4 (2013): 407-413.
- Xiong, Wu, et al. "Soil protist communities form a dynamic hub in the soil microbiome. (opens in new tab) " The ISME Journal 12.2 (2022): 634-638.
- Foissner, Wilhelm. "Protist diversity and distribution: some basic considerations. (opens in new tab) " Protist diversity and geographical distribution. Springer, Dordrecht, 2007. 1-viii.
What Are Protists That Have Animal Like Characteristics Called
Source: https://www.livescience.com/54242-protists.html




Comments
Post a Comment